These days, we are hearing about the escalation in the price of cocoa worldwide. This key ingredient in chocolate, cocoa, is experiencing a significant increase in its price in international markets. This increase has raised concerns among consumers and has led to speculations about the possible impact on the prices of cocoa-derived products.
Why is the price of cocoa rising?
The cocoa production in West Africa, especially in Ivory Coast and Ghana, two of the largest producers, has been low due to a combination of droughts and torrential rains.
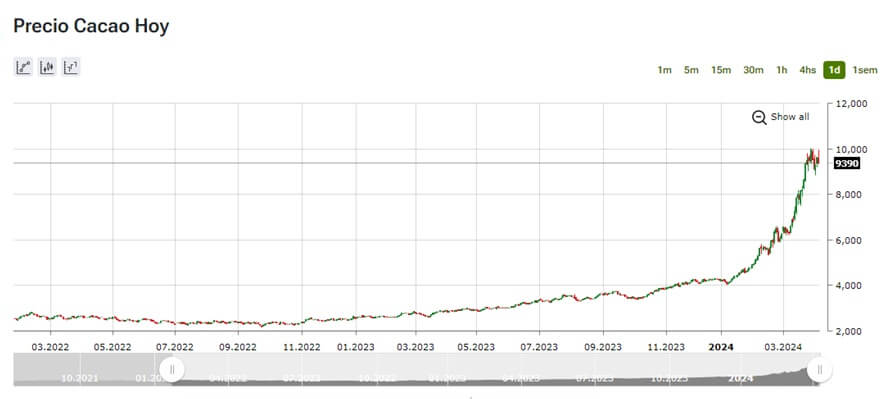
This situation has led to a 230% increase in cocoa prices over the last 12 months, reaching $10,000 per ton, a price never seen before. Additionally, the European Union has banned the import of foods produced on deforested land, adding pressure on cocoa availability.
Coca prices 09/04/2024 – IFCmarkets
Impact on cocoa-derived products
We have observed the evolution of some cocoa-containing products from September to April 2024.
In the case of Cola-Cao, there has been an average increase of 9% over these 6 months.
Chocolate Donettes have experienced an average increase of 6% over the same period.
Oreo cookies have risen by 7% since September, with most of the increase occurring this year.
Nestlé’s milk chocolate bar has increased by 11% in the last 6 months.
It is important to note that these products are not pure cocoa, so the impact of cocoa prices affects only a portion of the product. However, this increase adds to the widespread rise in food prices, particularly affecting sugar and flour, so it is expected that chocolate, candies, and other pastry products will increase in price.

What can we expect in the future?
It is highly possible that the increase in cocoa prices in international markets has not fully translated into the prices we pay in stores because manufacturers may be using previously purchased cocoa stocks until they are depleted.
Furthermore, major brands may have cocoa supply contracts at a fixed price for a certain period of time, so they may not yet be experiencing the rise in the current international market.
When these stocks are depleted and new contracts are signed, further increases are expected.
To mitigate these anticipated increases, manufacturers may seek resources to keep their prices competitive and avoid losing sales: limiting the amount of cocoa they use in their recipes, seeking new suppliers in other regions such as the Americas or Southeast Asia.